Introduction to China's Space Program
China's space program has been a cornerstone of the nation's technological advancement and international standing. Over the past few decades, China has made significant strides in space exploration, consistently launching satellites, probes, and manned missions. This article aims to provide an overview of China's space program, highlighting its continuous发射 (launches) and the advancements made in the field.
Historical Milestones
China's space program dates back to the 1950s when the country began investing in rocket technology. The first major milestone came in 1970 with the launch of the first Chinese satellite, Dongfanghong-1 (东方红一号). This marked the beginning of China's space era and set the stage for further exploration and development.
One of the most significant achievements was the successful launch of the Shenzhou (神舟) spacecraft, which carried China's first astronaut, Yang Liwei, into space in 2003. This marked China's entry into the exclusive club of countries capable of independently sending humans into space.
Continuous Launches of Satellites
China has a robust program for launching satellites, which serve various purposes such as communication, navigation, earth observation, and scientific research. The Chinese Long March (长征) series of rockets has been the backbone of these missions, with multiple launches taking place each year.
One of the most notable recent launches was the deployment of the BeiDou-3 (北斗三号) navigation satellite system. This global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is designed to provide positioning, navigation, and timing services worldwide. The final satellite was launched in 2020, completing the constellation and making China the fourth country to independently operate a GNSS after the United States, Russia, and the European Union.
Exploration Missions to Mars and Beyond
China's space program has not been limited to Earth orbit. The country has embarked on several missions aimed at exploring the solar system. The most ambitious of these was the launch of the Tianwen-1 (天问一号) mission in 2020, which consists of an orbiter, a lander, and a rover. The mission's goal is to explore Mars, making China the second country after the United States to land a rover on the Red Planet.
Additionally, China has plans to send a probe to the Moon, known as the Chang'e-5 (嫦娥五号) mission. This mission successfully returned lunar samples to Earth in 2020, marking a significant achievement in China's lunar exploration efforts.
Technological Advancements
China's space program has been a driver of technological innovation within the country. The development of the Long March rockets, satellite technology, and space exploration capabilities has required advancements in materials science, propulsion systems, and data processing.
One of the most notable technological breakthroughs was the development of China's own launch vehicle, the Long March 5, which is capable of carrying heavy payloads into space. This rocket has been instrumental in launching the country's space exploration missions, including the Tianwen-1 mission to Mars.
Collaboration and International Engagement
While China has made significant strides in its space program, it has also engaged in international collaboration. China has signed agreements with various countries for the sharing of data and technology. For example, the Chinese Academy of Sciences has collaborated with international research institutions to study the Earth's environment and climate change through satellite observations.
China has also been involved in international space missions, such as the International Space Station (ISS). While not a member of the ISS partnership, China has sent astronauts to the station through its own program, the Shenzhou program.
Future Prospects
The Chinese space program is poised for even greater achievements in the coming years. With the successful completion of the BeiDou system and the Mars mission, China is aiming to establish a permanent moon base and further explore the solar system.
China's commitment to space exploration is not only a testament to its technological prowess but also a reflection of its ambition to play a leading role in global space activities. As the country continues to launch missions and innovate in space technology, the world will undoubtedly witness more milestones in China's space journey.
Conclusion
China's space program has been marked by a series of continuous发射 (launches) that have propelled the nation into the ranks of space-faring nations. From the early days of the Dongfanghong-1 satellite to the recent achievements in the Mars mission, China's space program has been a testament to the country's dedication to scientific research and technological advancement. As China continues to push the boundaries of space exploration
转载请注明来自建筑资质代办_资格培训_上海积分落户,本文标题:《中国航天不断的发射英语,中国航天发展史的英文 》


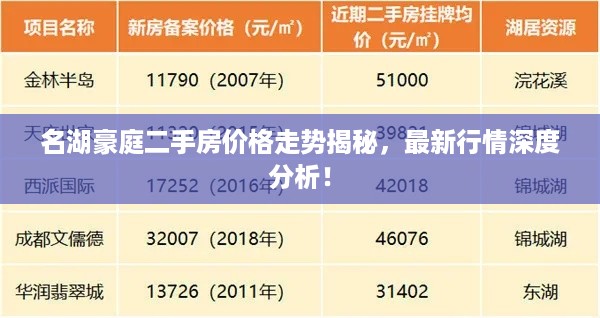






 蜀ICP备2022005971号-1
蜀ICP备2022005971号-1
还没有评论,来说两句吧...